What is a computer?

A computer is an electronic gadget that processes, stores, manipulates data, makes calculations, and generates results according to a set of instructions.
Types of computers
Super Computers

Supercomputers are high-performance computing systems. These are particularly designed to handle extremely large and complex calculations at incredibly fast speeds. Certainly, these are used for scientific and engineering tasks that require immense processing power, such as climate modeling, nuclear simulations, genomic research, artificial intelligence, and cryptography.
Mainframe Computers

Mainframe computers are powerful, large-scale machines. However, they are primarily used by large organizations for critical applications, bulk data processing (like census, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning), and transaction processing.
People know mainframes for their reliability, scalability, and security. Therefore, making them ideal for handling vast amounts of data and supporting thousands of simultaneous users.
Mini Computers

Minicomputers (also known as “midrange computers”) are a class of computers developed in the 1960s. These are more affordable and compact alternatives to mainframe computers. They are especially smaller, less powerful, and less expensive than mainframes, yet more powerful than early personal computers.
Although manufacturers designed minicomputers for tasks requiring more computing power than a microcomputer (like a PC), it certainly did not necessitate the vast capabilities of a mainframe.
Personal Computers

Personal Computers (PCs) are especially for individual use, making computing accessible and convenient for everyday tasks. However, they are intended for use by one person at a time and are versatile, affordable, and easy to operate. These computers are not only suitable for home but office environments.
Workstations Computers
Workstation computers are high-performance computing systems. These are especially for technical or specialized professional tasks that require significant computing power, reliability, and expandability.
Furthermore, workstations handle demanding applications such as 3D rendering, scientific simulations, complex data analysis, software development, engineering design, and multimedia production.
Server Computers

Moreover, Server computers (often referred to as servers) are specialized computers. These provide services, data, and resources to other computers, devices, or users over a network. Servers are the backbone of modern networks, whether small local area networks (LANs) or large-scale internet environments.
However, server computers often handle multiple simultaneous requests, run continuously, and provide high reliability, performance, and security levels.
Micro Computers

Microcomputers are designed for individual use. They are typically characterized by their small size, affordability, and use of microprocessors as their central processing unit (CPU).
Smartphones (Mobiles and tablets) come under microcomputers.
Parts of Computers
CPU (Central Processing Unit)

CPU Stands for “Central Processing Unit”, also called the processor. It is referred to as the brain of the computer. Moreover, the CPU performs all the tasks such as running applications, data handling, OS (Operating System), and other software.
SSD
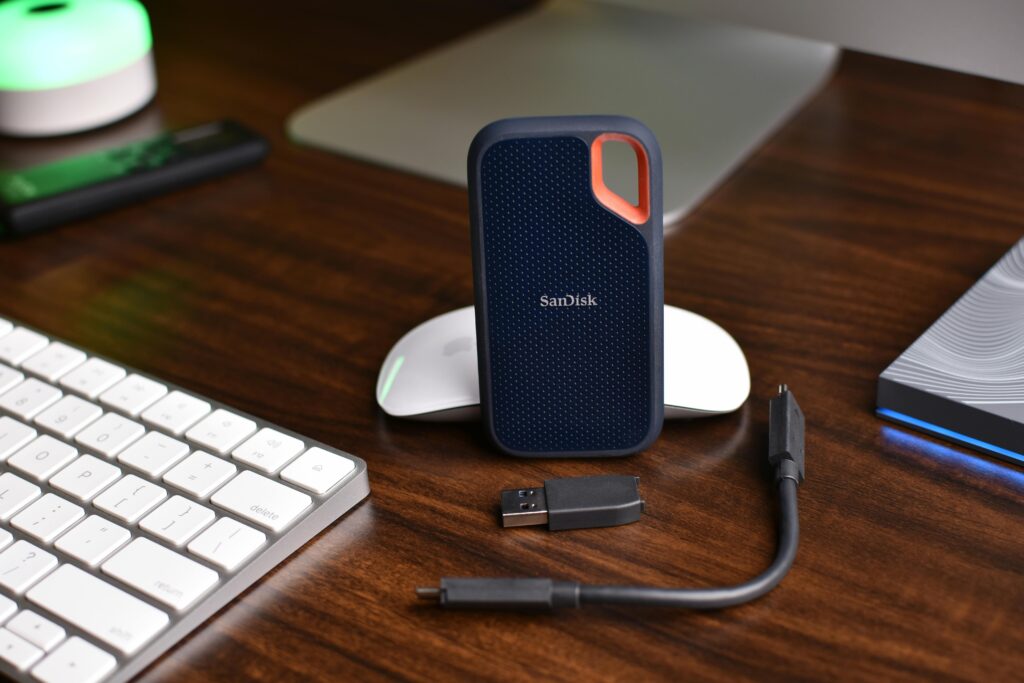

SSD stands for “Solid State Drive”. It uses flash memory to store the data of computers. These are faster than HDD (Hard Drives).
SSDs are commonly used in computers, laptops, servers, and other electronic devices
HDD
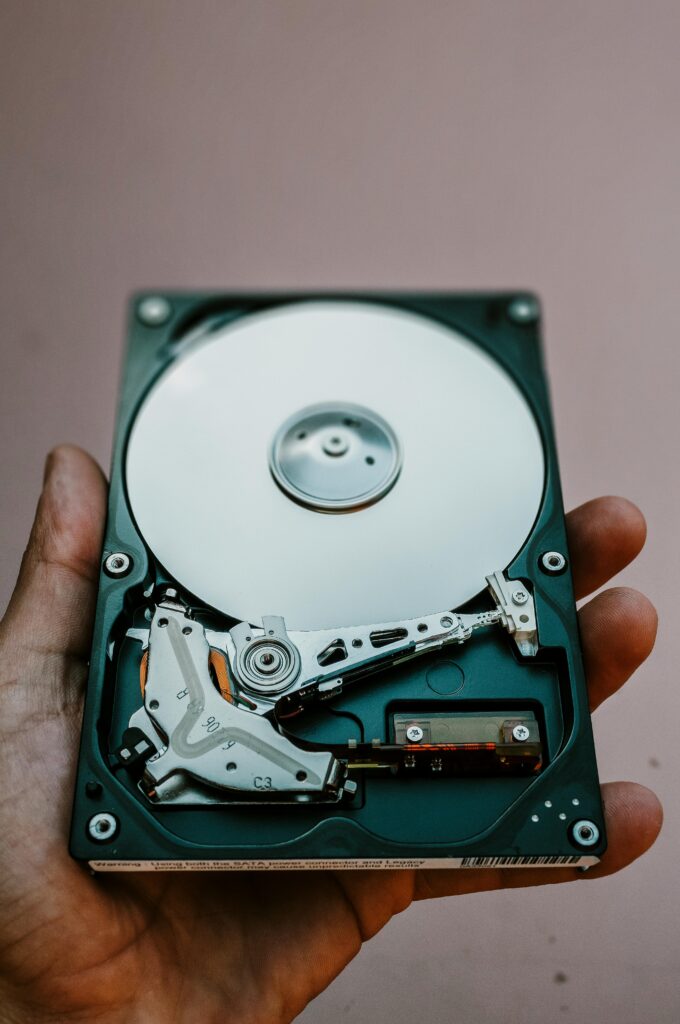

HDD stands for “Hard Disk Drives”. An HDD (Hard Disk Drive) is a traditional storage device. These are slower than SSDs.
HDDs have been widely used for decades in computers, laptops, servers, and other electronic devices.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
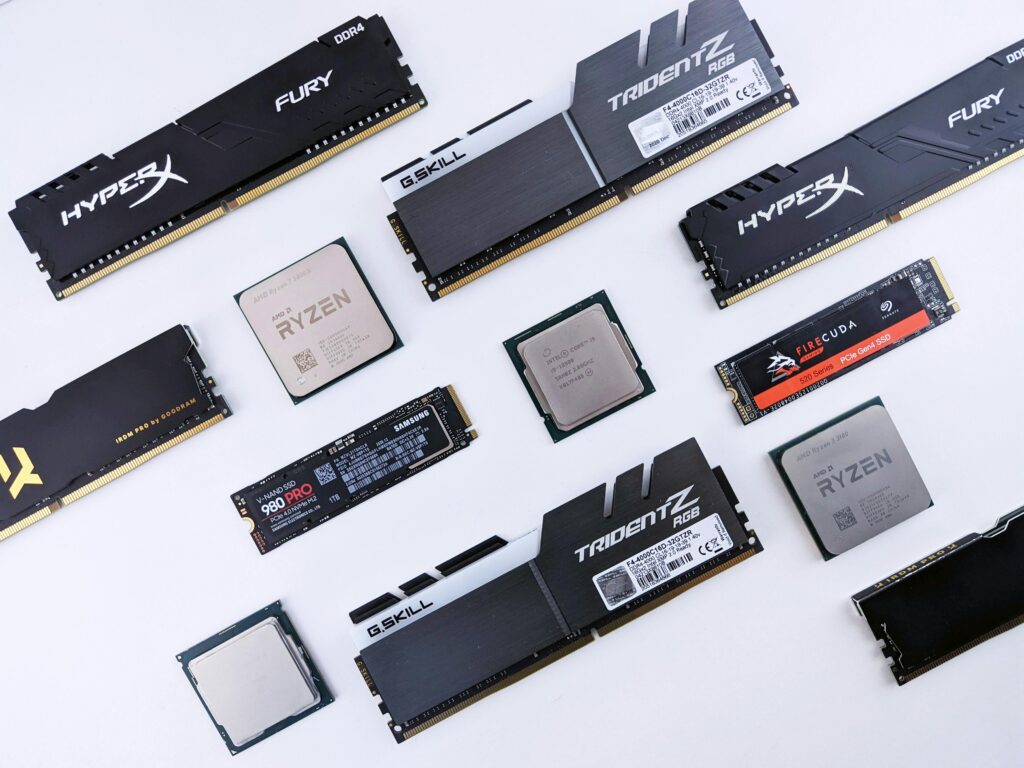

RAM Stands for “Random Access Memory”. It is a volatile memory. RAM is used in computers and other devices to store data temporarily that the CPU needs to access quickly.
RAM loses its contents when the computer is turned off.
Graphics Card
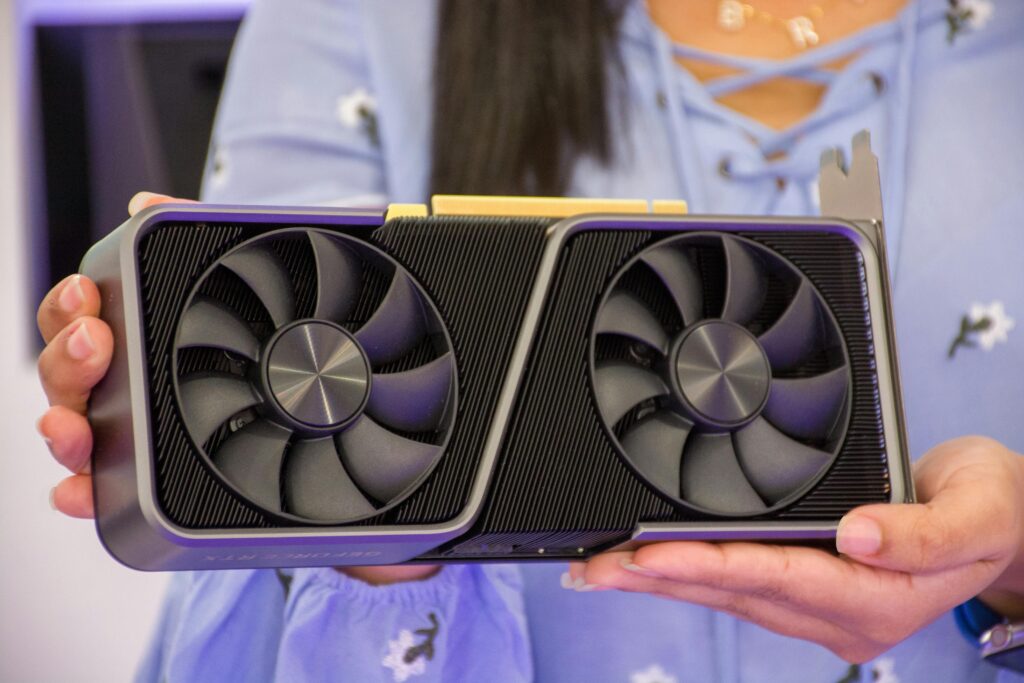

Graphics Card or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a hardware component responsible for rendering images, videos, and animations to your monitor.
A Graphics Card improves the overall visual performance, especially in graphics-intensive applications like gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
Cooling Fan
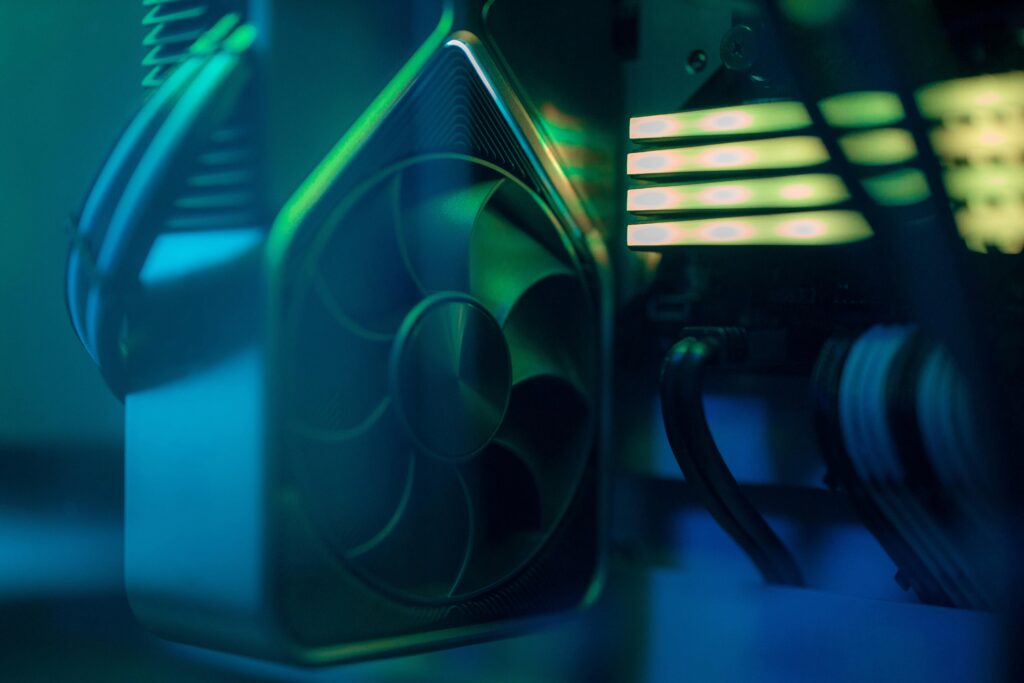

A cooling fan of computers dissipates heat generated by various computer components. Without a doubt, effective cooling is essential to maintain optimal performance, prevent overheating, and prolong the lifespan of the computers.
PSU (Power Supply Unit)
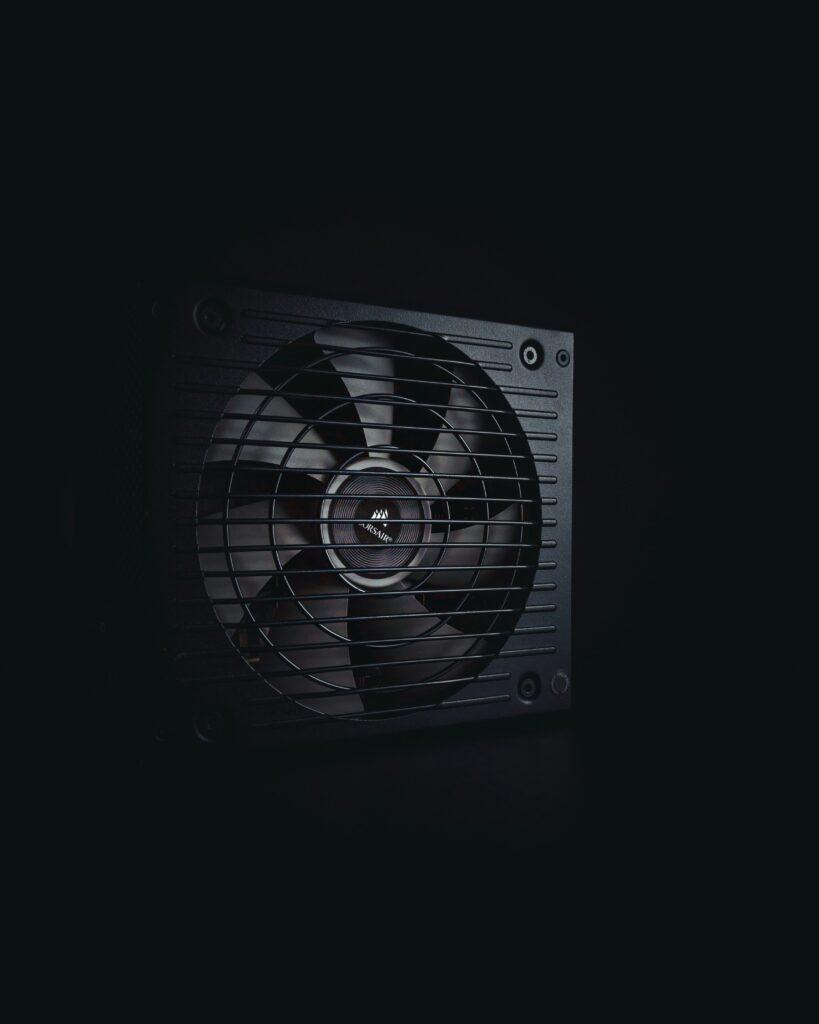

The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a crucial component of a computer. The PSU converts alternating current (AC) from the electrical outlet into direct current (DC).
More importantly, it distributes power to various components such as the motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and peripherals.
Uses of Computer
Personal Use

- Internet Browsing: Accessing websites, social media, and online content.
- Email: Communicating through email services.
- Entertainment: Streaming movies, music, and games.
- Productivity: Creating and editing documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
- Gaming: Playing video games, ranging from casual to high-performance gaming.
- Photo and Video Editing: Editing and managing personal photos and videos.
Business and Professional Use

- Data Management: Storing and analyzing business data, using databases and spreadsheets.
- Communication: Email, video conferencing, and collaboration tools.
- Accounting: Managing financial records, bookkeeping, and financial planning.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Handling customer interactions and data.
- Project Management: Planning, tracking, and managing projects using specialized software.
- Design and Creative Work: Graphic design, web design, and multimedia production.
Education

- E-Learning: Accessing online courses, educational resources, and virtual classrooms.
- Research: Conducting research using online databases and academic journals.
- Assignments and Projects: Creating and submitting academic work.
- Simulation and Modeling: Using software to simulate real-world scenarios and experiments.
Healthcare
- Medical Records: Managing electronic health records (EHR) and patient information.
- Telemedicine: Providing remote consultations and medical care.
- Medical Imaging: Analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and other medical images.
- Research and Development: Conducting research for new treatments and medical technologies.
Engineering and Science

- Simulations and Modeling: Performing complex simulations and models in fields like aerospace, civil engineering, and physics.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing large datasets using statistical and computational methods.
- Design: CAD (Computer-Aided Design) for creating detailed engineering designs and blueprints.
- Scientific Research: Conducting experiments and analyzing results using specialized software.
Government and Public Services

- Administrative Tasks: Managing public records, services, and internal operations.
- Public Communication: Providing information and services to the public through websites and online portals.
- Law Enforcement: Managing criminal records, investigations, and public safety systems.
Finance and Banking

- Transaction Processing: Managing financial transactions and account management.
- Stock Trading: Buying and selling stocks and other financial instruments.
- Risk Management: Analyzing financial risks and managing investments.
Manufacturing and Industry

- Automation: Controlling industrial processes and machinery.
- Supply Chain Management: Managing inventory, logistics, and production schedules.
- Quality Control: Monitoring and ensuring product quality through data analysis and automation.
Research and Development

- Innovations: Developing new technologies, software, and applications.
- Experimental Analysis: Using computational tools for experimentation and analysis.
Networking and Communication

- Network Management: Setting up and maintaining computer networks and internet connectivity.
- VoIP and Video Conferencing: Facilitating voice and video communication over the internet.
Security
- Cybersecurity: Protecting systems and data from cyber threats and attacks.
- Surveillance: Managing and analyzing security camera feeds and access control systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning

- AI Development: Creating and training AI models for various applications.
- Data Processing: Analyzing large datasets to train and deploy machine learning algorithms.

Pingback: What is Smartphone | Needs | Smartphones or Laptops